Dan Zambonini on Box UK, has made an excellent survey on different business models used in the Internet.
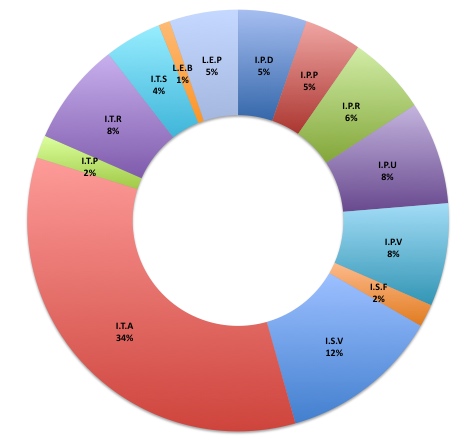
Chris Anderson, in his blog reports the news and notices that most of them are variations of ad-supported Free and Freemium. In the chart below, the largest segment (ITA) is ad-supported, the second largest (ISV) is Freemium. After that is referral (ITR) and then the sale of virtual goods (IPV), such as the gifts in Facebook.
Dan writes “We spent a few hours going through the Webware 100 Top Web Apps for 2008, analysing the business model(s) used by each. The chart below shows the results of this survey: 34% use Advertising, 12% a Variable Subscription model, and 8% each for Virtual Products (typically digital downloads), Related Products (typically a large software company offering a free product to attract you to their platform) and Pay-Per-Use.”
Business Models
| Model | Variation | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Immediate Revenue | Models for generating regular income, cash-flow (‘Self-Sufficient’ models) | |
| I.S | Subscription | Charge the end-user a regular, recurring fee. Consider:
|
|
| I.S.F | Fixed | A single, fixed subscription cost (e.g. to access an online magazine or a specific service). | |
| I.S.V | Variable | A number of fixed-price subscriptions are available to the end-user; fee dictates feature/usage limitations, etc. This includes the ‘Freemium’ model; a (usually limited) ‘free’ option alongside one or more paid options. | |
| I.T | Third-Party Supported | The end-user receives the service for free; a third-party pays the fee for a returned service. | |
| I.T.A | Advertising | One or more third-parties place clearly defined adverts within the website/application. Variations of adverts include graphical banners, text, inline, pop-over, interstitial, etc. Normally charged by cost per click, cost per action, or cost per thousand impressions. | |
| I.T.S | Sponsorship | One or more third parties become the ‘official’ sponsor(s) of the website. This could include fixed (non-rotating, typically prominent) adverts, integration of third-party branding (colours, slogans) and/or licensing agreements. | |
| I.T.C | Paid Content | Advertorials: third-parties pay to include marketing-led content on the website. | |
| I.T.P | Paid Placement | Third-parties pay to be included in lists or in the application (e.g. comparisons, reviews, entertainment listings). | |
| I.T.R | Referrer | End-users are directed to third-party sites, which pay a fee to the website owner for any referred transactions (e.g. comparison sites). | |
| I.T.L | License Content | Third-Parties are given access to re-use the content from the web-site for their own purposes. | |
| I.P | Payments | The end-user makes individual, ad-hoc transactional purchases. | |
| I.P.U | Pay-per-use | Micropayments: the end-user is charged a fee to use an online service (one-off, or for a limited time). This includes the ‘brokerage’ model, where user(s) are charged a fixed-price or percentage per transaction (e.g. ebay). This also includes the purchase of ‘credits’ e.g. 10 uses of the service for a fixed cost. Discounts can be offered for bulk purchases. | |
| I.P.P | Physical Products | The typical e-commerce model; includes books, CDs, holidays, tickets, etc. Typically each ‘physical product’ has a non-arbitrary cost associated with its production. | |
| I.P.V | Virtual Products | The end-user purchases a ‘digital’ product that typically has a negligible cost of replication. This includes virtual gifts (e.g. Facebook), in-game items (e.g. World of Warcraft), and other virtual assets (e.g. land in Second Life). | |
| I.P.R | Related Products | The end-user has free access to the main product/service. An additional, optional charge is made for related ‘added value’ products/services, e.g. documentation, support, commercial versions, related iPhone or Android application, etc. | |
| I.P.D | Donations | The website relies on voluntary end-user donations (e.g. a ‘Tip Jar’). | |
| L | Long-Term Revenue | Strategic, ‘Invest and Reward’ models where costs are incurred initially for a longer-term ‘pay off’. | |
| L.E | Establish and Exploit | Attract a substantial audience before monetizing. | |
| L.E.R | Re-use/Re-sell | Re-sell/re-use the data/content, usually from User Generated Content websites e.g. create books, posters or other purchasable products from data/content created on site. | |
| L.E.P | Platform | Establish a platform, then charge for third parties to participate once an audience has been established e.g. iPhone. See also Facebook. | |
| L.E.B | Branding | Build a ‘personal brand’ for yourself/your company. Once awareness is raised, go on Conference/Workshop/‘Expert’ circuit, or release a book, etc. | |
| L.S | Sell/Exit | Create a popular application/website, then make it someone else’s problem to monetize e.g. YouTube | |
Meta-Models
The following business models can be applied in addition to most of the basic revenue models described above.
| Model | Variation | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| M.R | Revenue Share | End-users are offered a cash incentive to make the website/application generate revenue, by sharing a percentage of revenue with them (usually based on their personal referrals or popularity of their content). | |
| M.R | Re-Seller | The end-user can re-sell the online service. | |
| M.R.A | Affiliate | The end-user is paid to direct customers to the website, typically by listing/selling the products/services elsewhere. | |
| M.R.W | White Label | The end-user can brand/tailor the online service and re-sell it as their own (typically taking a percentage of the generated revenue, or paying a fixed subscription cost to the original service). |
